Slots in D-Bus adaptors are declared just like normal, public slots, but their parameters must follow certain rules (see The Qt D-Bus Type System for more information). Slots whose parameters do not follow those rules or that are not public will not be accessible via D-Bus.
Given a PCI domain, bus, and slot/function number, the desired PCI device is located in the list of PCI devices. If the device is found, its reference count is increased and this function returns a pointer to its data structure. The caller must decrement the reference count by calling pcidevput. However, unless a card and slot are designed to use a wider bus (that is, 64 bits) or a faster bus speed (66 MHz) they generally default to the lower setting. For example, a 64-bit PCI card like Matrox P690 Plus LP PCI has an edge connector that's wider (longer) than for a 32-bit PCI card like Matrox G450x4 MMS. A bus is a large wheeled vehicle meant to carry many passengers along with the driver. It is larger than a car. The name is a shortened version of omnibus, which means 'for everyone' in Latin. Buses used to be called omnibuses, but people now simply call them 'buses'. There are many types of bus around the world.
A bus is a large wheeled vehicle meant to carry many passengers along with the driver. It is larger than a car. The name is a shortened version of omnibus, which means 'for everyone' in Latin.Buses used to be called omnibuses, but people now simply call them 'buses'. There are many types of bus around the world.
Slots can have one parameter of type const QDBusMessage &, which must appear at the end of the input parameter list, before any output parameters. This parameter, if present, will be initialized with a copy of the current message being processed, which allows the callee to obtain information about the caller, such as its connection name.
Slots can be of three kinds:
- Asynchronous
- Input-only
- Input-and-output
Asynchronous Slots
Asynchronous slots are those that do not normally return any reply to the caller. For that reason, they cannot take any output parameters. In most cases, by the time the first line of the slot is run, the caller function has already resumed working.
However, slots must not rely on that behavior. Scheduling and message-dispatching issues could change the order in which the slot is run. Code intending to synchronize with the caller should provide its own method of synchronization.
Asynchronous slots are marked by the keyword Q_NOREPLY in the method signature, before the void return type and the slot name. The quit() slot in the D-Bus Complex Ping Pong Example is an example of this.
Input-Only Slots
Input-only slots are normal slots that take parameters passed by value or by constant reference. However, unlike asynchronous slots, the caller is usually waiting for completion of the callee before resuming operation. Therefore, non-asynchronous slots should not block or should state it its documentation that they may do so.
Input-only slots have no special marking in their signature, except that they take only parameters passed by value or by constant reference. Optionally, slots can take a QDBusMessage parameter as a last parameter, which can be used to perform additional analysis of the method call message.
Input and Output Slots
Like input-only slots, input-and-output slots are those that the caller is waiting for a reply. Unlike input-only ones, though, this reply will contain data. Slots that output data may contain non-constant references and may return a value as well. However, the output parameters must all appear at the end of the argument list and may not have input arguments interleaved. Optionally, a QDBusMessage argument may appear between the input and the output arguments.
Automatic Replies
Is lots of discharge normal. Method replies are generated automatically with the contents of the output parameters (if there were any) by the Qt D-Bus implementation. Slots need not worry about constructing proper QDBusMessage objects and sending them over the connection.
However, the possibility of doing so remains there. Should the slot find out it needs to send a special reply or even an error, it can do so by using QDBusMessage::createReply() or QDBusMessage::createErrorReply() on the QDBusMessage parameter and send it with QDBusConnection::send(). The Qt D-Bus implementation will not generate any reply if the slot did so.
Warning: When a caller places a method call and waits for a reply, it will only wait for a limited amount of time. Slots intending to take a long time to complete should make that fact clear in documentation so that callers properly set higher timeouts.
Delayed Replies
In some circumstances, the called slot may not be able to process the request immediately. This is frequently the case when the request involves an I/O or networking operation which may block.
If this is the case, the slot should return control to the application's main loop to avoid freezing the user interface, and resume the process later. To accomplish this, it should make use of the extra QDBusMessage parameter at the end of the input parameter list and request a delayed reply.

We do this by writing a slot that stores the request data in a persistent structure, indicating to the caller using QDBusMessage::setDelayedReply(true) that the response will be sent later.
The use of QDBusConnection::sessionBus().send(data->reply) is needed to explicitly inform the caller that the response will be delayed. In this case, the return value is unimportant; we return an arbitrary value to satisfy the compiler.
When the request is processed and a reply is available, it should be sent using the QDBusMessage object that was obtained. In our example, the reply code could be something as follows:
As can be seen in the example, when a delayed reply is in place, the return value(s) from the slot will be ignored by Qt D-Bus. They are used only to determine the slot's signature when communicating the adaptor's description to remote applications, or in case the code in the slot decides not to use a delayed reply.
Bus Slot Type
The delayed reply itself is requested from Qt D-Bus by calling QDBusMessage::reply() on the original message. It then becomes the resposibility of the called code to eventually send a reply to the caller.
Warning: When a caller places a method call and waits for a reply, it will only wait for a limited amount of time. Slots intending to take a long time to complete should make that fact clear in documentation so that callers properly set higher timeouts.
See also Using Qt D-Bus Adaptors, Declaring Signals in D-Bus Adaptors, The Qt D-Bus Type System, QDBusConnection, and QDBusMessage.

© 2021 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Computer bus is a subsystem that transfers data between components inside a computer or between computers.
Modern computer buses can use parallel and bit-serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop (electrical parallel) or daisy chain topology, or connected by switched hubs, as in the case of USB.
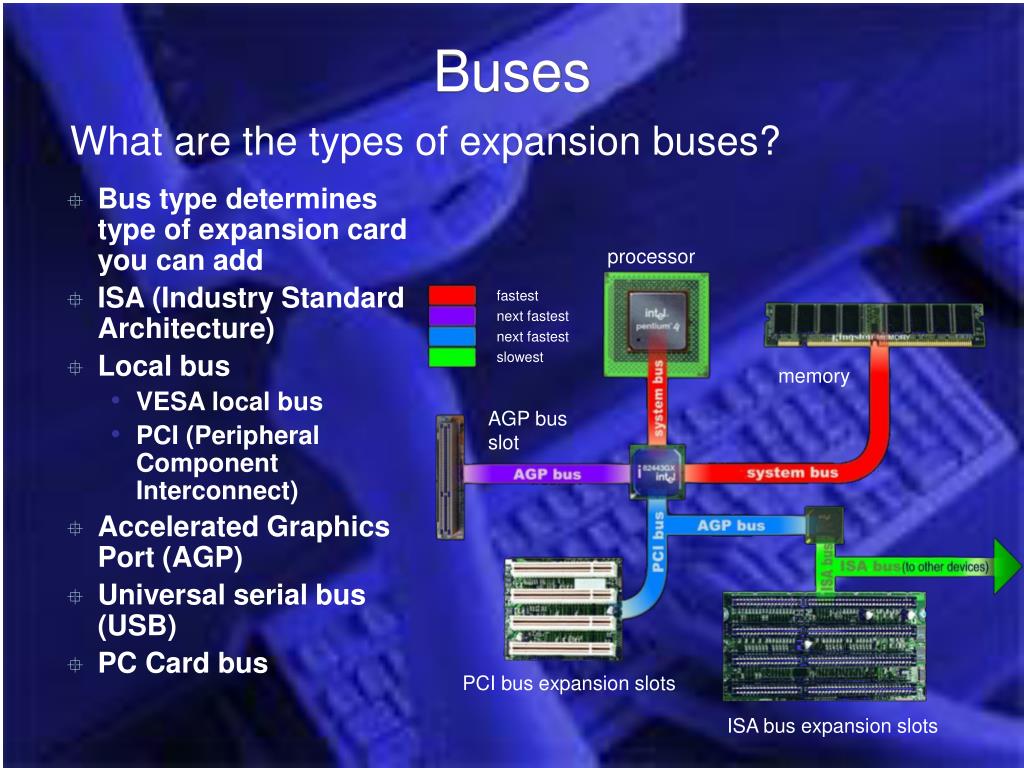
Pci Bus Slot Types
Forward to / Apple / Asus pinouts or follow to 33 OLD hardware pinouts.
See also RS-232 and other serial ports and interfaces pinouts

Input-only slots have no special marking in their signature, except that they take only parameters passed by value or by constant reference. Optionally, slots can take a QDBusMessage parameter as a last parameter, which can be used to perform additional analysis of the method call message.
Input and Output Slots
Like input-only slots, input-and-output slots are those that the caller is waiting for a reply. Unlike input-only ones, though, this reply will contain data. Slots that output data may contain non-constant references and may return a value as well. However, the output parameters must all appear at the end of the argument list and may not have input arguments interleaved. Optionally, a QDBusMessage argument may appear between the input and the output arguments.
Automatic Replies
Is lots of discharge normal. Method replies are generated automatically with the contents of the output parameters (if there were any) by the Qt D-Bus implementation. Slots need not worry about constructing proper QDBusMessage objects and sending them over the connection.
However, the possibility of doing so remains there. Should the slot find out it needs to send a special reply or even an error, it can do so by using QDBusMessage::createReply() or QDBusMessage::createErrorReply() on the QDBusMessage parameter and send it with QDBusConnection::send(). The Qt D-Bus implementation will not generate any reply if the slot did so.
Warning: When a caller places a method call and waits for a reply, it will only wait for a limited amount of time. Slots intending to take a long time to complete should make that fact clear in documentation so that callers properly set higher timeouts.
Delayed Replies
In some circumstances, the called slot may not be able to process the request immediately. This is frequently the case when the request involves an I/O or networking operation which may block.
If this is the case, the slot should return control to the application's main loop to avoid freezing the user interface, and resume the process later. To accomplish this, it should make use of the extra QDBusMessage parameter at the end of the input parameter list and request a delayed reply.
We do this by writing a slot that stores the request data in a persistent structure, indicating to the caller using QDBusMessage::setDelayedReply(true) that the response will be sent later.
The use of QDBusConnection::sessionBus().send(data->reply) is needed to explicitly inform the caller that the response will be delayed. In this case, the return value is unimportant; we return an arbitrary value to satisfy the compiler.
When the request is processed and a reply is available, it should be sent using the QDBusMessage object that was obtained. In our example, the reply code could be something as follows:
As can be seen in the example, when a delayed reply is in place, the return value(s) from the slot will be ignored by Qt D-Bus. They are used only to determine the slot's signature when communicating the adaptor's description to remote applications, or in case the code in the slot decides not to use a delayed reply.
Bus Slot Type
The delayed reply itself is requested from Qt D-Bus by calling QDBusMessage::reply() on the original message. It then becomes the resposibility of the called code to eventually send a reply to the caller.
Warning: When a caller places a method call and waits for a reply, it will only wait for a limited amount of time. Slots intending to take a long time to complete should make that fact clear in documentation so that callers properly set higher timeouts.
See also Using Qt D-Bus Adaptors, Declaring Signals in D-Bus Adaptors, The Qt D-Bus Type System, QDBusConnection, and QDBusMessage.
© 2021 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Computer bus is a subsystem that transfers data between components inside a computer or between computers.
Modern computer buses can use parallel and bit-serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop (electrical parallel) or daisy chain topology, or connected by switched hubs, as in the case of USB.
Pci Bus Slot Types
Forward to / Apple / Asus pinouts or follow to 33 OLD hardware pinouts.
See also RS-232 and other serial ports and interfaces pinouts
- CardBus32-bit bus defined by PCMCIA.
- CompactPCI busPCI=Peripheral Component Interconnect. CompactPCI is a version of PCI adapted for industrial and/or embedded applications.
- FireWire (IEEE1394) bus interfaceDefined by IEEE 1394-1995 standard as a serial data transfer protocol and interconnection system. Also known as iLink (Sony) or Lynx. Often implemented in consumer electronics devices, digital video cameras, VCRs, some other multimedia hardware and computers.
- IndustrialPCI busPCI=Peripheral Component Interconnect. IndustrialPCI is a version of PCI adapted for industrial and/or embedded applications.
- Mini PCI busMini PCI is an alternate PCI implementation designed for small form factor. It´s specification is a sub-set of PCI standard using 100 pin (Type I/II) or 124 pin (Type III) connector.
- PC/104 busPC/104 is a compact version of the ISA bus. PC/104 is intended for specialized embedded computing environments where applications depend on reliable data acquisition despite an often extreme environment.
- PCI busThe PCI Bus is a high performance bus for interconnecting chips, expansion boards, and processor/memory subsystems.
- PCI Express 1x, 4x, 8x, 16x busPCI Express (PCIe, PCI-e) is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard.
- PCI Express Mini Card (Mini PCIe)
- PCMCIA (PC Card) busThe PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Card International Association) 16 bit bus
- USBUSB (Universal Serial Bus) designed to connect peripherals such as mice, keyboards, scanners, digital cameras, printers, hard disks, and networking components to PC. It has become the standard connection method for wide variety of devices.
- USB 3.0 connectorUSB 3.0 is the successor of USB 2.0. USB 3 reduces the time required for data transmission, reduces power consumption, and is backward compatible with USB 2.0
- USB Type C
- VME64x bus
- VMEbusVMEbus is a computer bus standard originally developed for the Motorola 68000 line of CPUs, but later widely used for many applications.
Apple Pinouts
- Apple Duo DockAvailable on Apple Duo Dock & Duo Dock II dockingstations. For use with Apple PowerBook Duo computers.
Asus Pinouts
Bus Slot Types
- ASUS PCI Express x1 / SupremeFX Combo slotThis slot is combo-connector that allow use of PCI Express cards or special ASUS proprietary codec cards such as SupremeFX X-Fi or SupremeFX II.
